Uterine cancer, often referred to as endometrial cancer, is a type of cancer that begins in the uterus, the pear-shaped organ where fetal development occurs. Detecting this cancer early significantly improves treatment outcomes, and one of the key diagnostic tools used in this process is the ultrasound.

What is Uterine Cancer?
Uterine cancer primarily originates from the endometrium, the lining of the uterus. It is most commonly diagnosed in postmenopausal women, although it can occur in younger women as well. Risk factors include obesity, hormone replacement therapy, tamoxifen use, a history of breast or ovarian cancer, and certain hereditary conditions such as Lynch syndrome.
Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Common symptoms of uterine cancer include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Pain during intercourse
- Difficulty urinating or frequent urination
Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosing Uterine Cancer
An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create pictures of the internal organs. For uterine cancer, the two main types of ultrasound used are transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound.
Transabdominal Ultrasound
This type of ultrasound involves placing the transducer on the abdomen. It helps visualize the uterus, ovaries, and surrounding structures. However, it may not provide as detailed images as the transvaginal ultrasound.
Transvaginal Ultrasound
In this procedure, a specially designed transducer is inserted into the vagina. This allows for a closer view of the uterus and its lining, providing detailed images of the endometrium. This method is particularly useful in assessing the thickness of the endometrium and identifying abnormalities.
What to Expect During an Ultrasound
During a transabdominal ultrasound, you will lie on your back while a technician applies a gel to your abdomen and moves the transducer over the area. For a transvaginal ultrasound, the transducer is inserted into the vagina. Both procedures are generally painless, although the transvaginal ultrasound might cause slight discomfort.
Interpreting the Ultrasound Results
An abnormal ultrasound can show various signs that may indicate uterine cancer, including:
- Thickened endometrium: A thickened endometrial lining can be a sign of endometrial hyperplasia or cancer.
- Irregular or heterogeneous endometrium: Uneven or mixed texture in the endometrium may suggest malignancy.
- Presence of masses or lesions: Detectable growths within the uterus may be indicative of cancer.
If abnormalities are detected, further diagnostic procedures such as endometrial biopsy or hysteroscopy may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of uterine cancer significantly improves the prognosis. Regular gynecological exams and prompt attention to abnormal symptoms are crucial. Ultrasound serves as a vital tool in the initial evaluation and helps guide subsequent diagnostic and treatment decisions.

Ultrasound imaging plays a critical role in the early detection and diagnosis of uterine cancer. Understanding the signs and symptoms of uterine cancer, combined with timely medical consultation and appropriate use of ultrasound, can lead to early intervention and more effective treatment. If you experience any abnormal symptoms, such as unusual bleeding or pelvic pain, consult your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Treatment Options for Uterine Cancer
Once uterine cancer is diagnosed, the treatment plan depends on the stage and grade of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. The main treatment options include:
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for uterine cancer. The most common surgical procedure is a hysterectomy, which involves the removal of the uterus. Depending on the spread of the cancer, a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes) and lymph node dissection may also be performed.

Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. There are two main types of radiation therapy used for uterine cancer:
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT): This involves directing radiation from outside the body onto the cancerous area.
- Brachytherapy: This involves placing radioactive material inside the vagina near the cancer cells.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is used to block the hormones that fuel cancer growth. This treatment is particularly effective for cancers that are hormone receptor-positive. Progesterone and other hormone-blocking medications can be used to slow the growth of the cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It is typically used for advanced-stage uterine cancer or when the cancer has spread beyond the uterus. Chemotherapy can be administered orally or intravenously and is often used in combination with other treatments.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy involves drugs that specifically target the cancer cells while sparing normal cells. These drugs interfere with specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Targeted therapies are becoming more common and may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
After treatment, regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence. Follow-up care typically includes:
- Physical exams
- Pelvic exams
- Imaging tests (such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs)
- Blood tests
Patients should also report any new symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately.
Coping with Uterine Cancer
A diagnosis of uterine cancer can be overwhelming. It is important to seek support from healthcare professionals, counselors, and support groups. Many resources are available to help patients and their families cope with the emotional and physical challenges of cancer.
Preventive Measures
While there is no sure way to prevent uterine cancer, certain lifestyle changes and medical interventions can reduce the risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for uterine cancer.
- Use of oral contraceptives: Long-term use of birth control pills has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer.
- Manage chronic conditions: Proper management of conditions such as diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can help lower risk.
- Routine screenings: Regular gynecological exams and prompt investigation of abnormal symptoms can lead to early detection.
Uterine cancer is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. Ultrasound is a crucial tool in detecting abnormalities in the uterus that may indicate cancer. Understanding the symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options can empower patients to take proactive steps in managing their health. Regular medical check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can aid in the prevention and early detection of uterine cancer, leading to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
References and Further Reading
For more detailed information on uterine cancer, its diagnosis, and treatment, consider consulting the following resources:
- American Cancer Society (www.cancer.org)
- National Cancer Institute (www.cancer.gov)
- Mayo Clinic (www.mayoclinic.org)
- World Health Organization (www.who.int)
If you have any concerns or symptoms related to uterine cancer, do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and personalized care plan.
Living with Uterine Cancer: Support and Resources
Living with uterine cancer involves more than just medical treatment; it also requires emotional, psychological, and practical support. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Emotional and Psychological Support
Counseling and Therapy: Professional counseling can help patients navigate the emotional challenges of a cancer diagnosis. Therapy can provide coping strategies, emotional support, and a safe space to express feelings.
Support Groups: Joining a support group allows patients to connect with others who are going through similar experiences. Sharing stories, advice, and encouragement can be incredibly beneficial.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
Practical Support
Nutritional Guidance: A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining strength and energy during cancer treatment. Consulting with a nutritionist can help patients develop a diet plan tailored to their needs.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve physical health and reduce fatigue. It’s important to discuss any new exercise routines with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and appropriate.
Financial Assistance: Cancer treatment can be costly. Patients should explore options for financial aid, insurance coverage, and support from nonprofit organizations that assist with medical expenses.
Advances in Uterine Cancer Research
Ongoing research continues to improve our understanding of uterine cancer and enhance treatment options. Some promising areas of research include:
Genetic Testing and Personalized Medicine: Advances in genetic testing allow for more personalized treatment plans based on the genetic makeup of the tumor. This approach can lead to more effective and targeted therapies.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. This treatment has shown promise in other types of cancer and is being explored for uterine cancer.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques: New surgical techniques, such as robotic-assisted surgery, offer less invasive options for removing tumors. These methods can reduce recovery time and minimize complications.
New Drug Developments: Researchers are continually developing and testing new drugs that target specific pathways involved in cancer growth. These drugs aim to be more effective with fewer side effects.
Preventive Strategies and Early Detection
While we cannot completely prevent uterine cancer, certain strategies can help reduce the risk:
Regular Screenings and Check-Ups: Regular gynecological exams can help detect abnormalities early. Discuss with your doctor how often you should be screened, especially if you have risk factors.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly can reduce the risk of many cancers, including uterine cancer.
Managing Risk Factors: If you have conditions that increase your risk of uterine cancer, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or obesity, managing these conditions can help lower your risk.
Hormonal Management: Using birth control pills, under the guidance of a healthcare provider, has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer.
Uterine cancer, while serious, is a condition that can be effectively managed with early detection and appropriate treatment. Ultrasound imaging is a critical tool in diagnosing abnormalities in the uterus and guiding further diagnostic and therapeutic steps. Understanding the symptoms, undergoing regular screenings, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key components in the fight against uterine cancer.
Patients diagnosed with uterine cancer should seek comprehensive care that includes not only medical treatment but also emotional and practical support. Advances in research continue to improve treatment options and outcomes, offering hope to those affected by this disease.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of uterine cancer, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. Early intervention can make a significant difference in treatment efficacy and overall prognosis. Remember, staying informed and proactive about your health is the best defense against cancer.
Additional Resources
For more information and support, consider reaching out to these organizations:
- American Cancer Society: www.cancer.org
- National Cancer Institute: www.cancer.gov
- Mayo Clinic: www.mayoclinic.org
- World Health Organization: www.who.int
- CancerCare: www.cancercare.org
- Foundation for Women’s Cancer: www.foundationforwomenscancer.org
These organizations offer a wealth of information on uterine cancer, including treatment options, support services, and the latest research developments. Your healthcare provider can also offer personalized advice and support tailored to your specific situation.
Navigating Life After Treatment
Life after treatment for uterine cancer can bring its own set of challenges and adjustments. Here are some important considerations for survivors:
Physical Recovery
Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring any signs of recurrence and managing long-term side effects. These visits typically include physical exams, imaging tests, and sometimes lab work.
Managing Side Effects: Side effects from treatment can vary widely. Common issues include fatigue, menopausal symptoms, and lymphedema. It’s important to communicate any side effects to your healthcare team so they can help manage them effectively.
Healthy Lifestyle: Continuing to maintain a healthy lifestyle is important for overall well-being and reducing the risk of other health issues. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Emotional and Psychological Well-Being
Mental Health Support: Many cancer survivors experience anxiety, depression, or fear of recurrence. Mental health professionals, such as counselors or therapists, can provide strategies to cope with these feelings.
Support Networks: Staying connected with family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation. Online forums and local support groups can be valuable resources.
Mindfulness and Stress Management: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and relaxation techniques can help manage stress and improve emotional health.
Long-Term Surveillance
Awareness of Symptoms: Being aware of and promptly reporting any new or unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider is important. Symptoms to watch for include unexplained bleeding, pelvic pain, or any significant changes in health.
Education and Advocacy: Staying informed about your health and being an advocate for yourself is empowering. Understanding your treatment history and potential long-term effects can help you manage your health proactively.
Family Planning and Fertility Considerations
For younger women diagnosed with uterine cancer, fertility can be a major concern. Here are some considerations:
Fertility Preservation: If you are of childbearing age and wish to have children in the future, discuss fertility preservation options with your healthcare provider before starting treatment. Options may include egg or embryo freezing.
Alternative Options: If fertility preservation is not possible or was not done, consider alternative family-building options such as adoption or surrogacy.
Hormone Replacement Therapy: In cases where treatment has induced early menopause, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) might be an option to manage symptoms. Discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
Advocacy and Awareness
Many survivors find purpose and fulfillment in advocating for cancer awareness and supporting others going through similar experiences. Here are ways to get involved:
Join Advocacy Groups: Many organizations welcome survivors who want to share their stories and advocate for better cancer research and care.
Participate in Fundraising: Fundraising events, such as walks, runs, and charity drives, raise money for cancer research and patient support services.
Share Your Story: Sharing your journey through blogs, social media, or speaking engagements can provide hope and support to others.
Surviving uterine cancer involves not only overcoming the disease but also adapting to life after treatment. With regular follow-up care, support from loved ones, and a proactive approach to health, survivors can lead fulfilling lives. Staying informed and involved in your care, connecting with support networks, and considering your long-term health and well-being are key components of navigating life after uterine cancer.
If you have been affected by uterine cancer or know someone who has, remember that resources and support are available. Whether through medical professionals, support groups, or advocacy organizations, help is out there. You are not alone in this journey, and with the right support and information, you can continue to live a healthy and fulfilling life.
Understanding the Importance of Research and Clinical Trials
Continuous research and participation in clinical trials play a vital role in advancing the understanding and treatment of uterine cancer. Here’s why they are important:
Contributions to Medical Knowledge
Innovation in Treatment: Clinical trials test new treatments, drugs, and therapies that could be more effective or have fewer side effects than current options. This innovation can lead to significant improvements in patient outcomes.
Understanding Disease Mechanisms: Research helps scientists understand the underlying mechanisms of uterine cancer, including genetic and environmental factors that contribute to its development. This knowledge can lead to better prevention strategies.
Improving Quality of Life: Trials often explore ways to reduce side effects and improve the quality of life for cancer patients, addressing both physical and emotional well-being.
Patient Participation in Clinical Trials
Access to Cutting-Edge Treatments: Patients participating in clinical trials may have access to new treatments that are not yet widely available. This can be particularly beneficial for those with advanced or treatment-resistant cancer.
Contributing to Future Treatments: By participating in clinical trials, patients contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge, potentially helping future patients receive better treatments.
Safety and Ethics: Clinical trials are conducted under strict regulatory guidelines to ensure patient safety. Ethical oversight committees review the study protocols to protect participants’ rights and well-being.
Personalized Medicine in Uterine Cancer Treatment
Personalized or precision medicine is an emerging approach in cancer treatment that tailors medical care to the individual characteristics of each patient. Here’s how it applies to uterine cancer:
Genetic Profiling
Tumor Analysis: Analyzing the genetic makeup of a tumor can provide valuable information about the mutations driving cancer growth. This analysis helps in selecting targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective.
Family History: Understanding genetic predispositions through family history can also inform treatment decisions and preventive measures for at-risk individuals.
Targeted Therapies
Specific Targets: Targeted therapies focus on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These treatments can be more effective and have fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Examples of Targeted Drugs: Drugs like PARP inhibitors and hormone therapies target specific pathways and receptors involved in uterine cancer. Ongoing research continues to develop and refine these options.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in managing uterine cancer, from diagnosis through treatment and follow-up care. Here’s how they support patients:
Multidisciplinary Teams
Comprehensive Care: A multidisciplinary team approach ensures that all aspects of a patient’s care are addressed. This team may include oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, pathologists, nurses, and social workers.
Coordinated Treatment Plans: Collaboration among different specialists leads to a well-coordinated treatment plan that is tailored to the patient’s needs.
Patient Education and Communication
Informed Decisions: Healthcare providers educate patients about their diagnosis, treatment options, and potential side effects, enabling them to make informed decisions about their care.
Open Communication: Maintaining open communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential for effective treatment. Patients should feel comfortable asking questions and expressing concerns.
Community and Advocacy Support
Building a strong support system and engaging with advocacy groups can significantly enhance the journey through uterine cancer:
Community Resources
Local Support Groups: Many communities offer local support groups where patients and survivors can share experiences and support each other.
Online Forums: Online forums and social media groups provide a platform for connecting with others globally, sharing advice, and finding emotional support.
Advocacy and Awareness
Raising Awareness: Advocacy groups work to raise awareness about uterine cancer, promoting early detection and supporting research funding.
Legislative Advocacy: These groups also work to influence healthcare policies, ensuring that cancer patients have access to necessary treatments and support services.
The journey through uterine cancer is challenging, but with the right support, knowledge, and resources, patients can navigate this path more effectively. Ongoing research, personalized medicine, and the dedication of healthcare providers contribute to improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this disease.
Staying informed, proactive, and connected to support networks can empower patients to manage their health and well-being. Whether you are a patient, a survivor, or a loved one, remember that there are many resources available to help you through this journey. Together, we can continue to make strides in the fight against uterine cancer, bringing hope and better outcomes to those affected.
Coping with the Emotional Impact of Uterine Cancer
Dealing with a uterine cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. It’s important to acknowledge and address these feelings as part of the healing process.
Common Emotional Responses
Fear and Anxiety: It’s normal to feel scared and anxious about the diagnosis, treatment, and future. Fear of the unknown can be particularly challenging.
Depression: Feelings of sadness and hopelessness can arise, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life.
Anger and Frustration: Some patients may feel angry about their diagnosis or frustrated by the limitations imposed by their illness and treatment.
Isolation: Cancer can sometimes make patients feel isolated from friends and family, especially if they are unable to participate in normal activities.
Strategies for Emotional Well-Being
Seek Professional Help: Counselors, therapists, and psychologists specializing in cancer care can provide valuable support. They offer coping strategies and a safe space to express emotions.
Join Support Groups: Connecting with others who have had similar experiences can provide comfort and understanding. Support groups can be found in person or online.
Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and improve emotional health.
Stay Connected: Maintain relationships with family and friends. Social support is crucial for emotional well-being.
Express Yourself: Writing in a journal, creating art, or engaging in hobbies can be therapeutic and provide an outlet for emotions.
Financial and Practical Considerations
The financial impact of a cancer diagnosis can be significant. It’s important to address these issues early on to reduce stress and focus on recovery.
Financial Assistance
Insurance: Review your insurance policy to understand what treatments and services are covered. Work with your healthcare provider’s billing department to manage claims.
Financial Aid Programs: Many organizations offer financial assistance for cancer patients, covering costs such as treatment, medications, and transportation.
Grants and Scholarships: Look for grants and scholarships specifically for cancer patients and survivors. These can help cover various expenses, including educational and living costs.
Practical Support
Transportation and Lodging: If you need to travel for treatment, look into programs that provide free or reduced-cost transportation and lodging.
Home Care Services: If you need help at home, services are available to assist with daily activities, medical needs, and personal care.
Legal Assistance: Legal aid organizations can help with issues such as employment rights, disability benefits, and estate planning.
Nutritional Support and Healthy Living
Maintaining good nutrition and a healthy lifestyle can support recovery and overall well-being during and after treatment.
Dietary Considerations
Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients that support healing.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important, especially during treatment. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Managing Side Effects: Treatment can cause side effects like nausea, loss of appetite, and taste changes. Work with a dietitian to find foods that are appealing and easy to digest.
Supplements: Discuss any supplements with your healthcare provider to ensure they do not interfere with treatment.
Physical Activity
Stay Active: Regular physical activity can improve energy levels, reduce fatigue, and enhance overall well-being. Choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or yoga.
Tailored Exercise Plan: Work with your healthcare provider or a physical therapist to create an exercise plan that suits your needs and abilities.
Survivorship and Long-Term Health
After treatment, it’s important to focus on long-term health and wellness. Here are some key considerations:
Regular Health Check-Ups
Follow-Up Appointments: Keep up with regular follow-up visits to monitor for any signs of recurrence and manage long-term side effects.
Screenings: Continue with routine screenings and tests as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Health Maintenance
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption to support overall health.
Chronic Condition Management: If you have other chronic conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, work with your healthcare provider to manage these effectively.
Navigating life with uterine cancer involves addressing not only the medical aspects but also the emotional, financial, and practical challenges. With comprehensive care, support networks, and a proactive approach to health, patients can manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Staying informed, seeking support, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key components of living well with and beyond uterine cancer. Remember, you are not alone on this journey. Numerous resources and support systems are available to help you through every step of the way. With the right care and support, you can face the challenges of uterine cancer with strength and resilience.
The Role of Caregivers in Uterine Cancer Journey
Caregivers play a vital role in the journey of someone diagnosed with uterine cancer. Their support can significantly impact the patient’s physical and emotional well-being.
Responsibilities of Caregivers
Emotional Support: Offering a listening ear, providing comfort, and maintaining a positive outlook can help patients cope with their emotions.
Physical Care: Assisting with daily activities, managing medications, and helping with mobility and personal care are critical tasks.
Medical Advocacy: Attending medical appointments, keeping track of treatments and medications, and communicating with healthcare providers ensure that the patient receives appropriate care.
Practical Assistance: Managing household chores, running errands, and providing transportation can help reduce the patient’s stress and allow them to focus on recovery.
Self-Care for Caregivers
Caregiving can be demanding, both physically and emotionally. It’s essential for caregivers to take care of themselves to avoid burnout.
Seek Support: Joining a caregiver support group can provide emotional support and practical advice from others in similar situations.
Take Breaks: It’s important to take regular breaks and make time for personal interests and relaxation.
Maintain Health: Eating well, exercising, and getting enough sleep are crucial for maintaining health and energy levels.
Ask for Help: Don’t hesitate to seek assistance from other family members, friends, or professional caregivers when needed.
Integrative and Complementary Therapies
Integrative therapies can complement conventional treatments and help improve the overall well-being of uterine cancer patients.
Types of Integrative Therapies
Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique can help manage pain, nausea, and other side effects of cancer treatment.
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can reduce stress, alleviate pain, and improve relaxation and overall quality of life.
Aromatherapy: The use of essential oils can enhance relaxation and provide emotional relief.
Mind-Body Practices: Techniques such as tai chi, yoga, and meditation promote physical and emotional healing.
Safety and Efficacy
Consult Healthcare Providers: Always discuss any integrative or complementary therapies with your healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and won’t interfere with conventional treatments.
Certified Practitioners: Ensure that any therapy is administered by a certified and experienced practitioner.
Advances in Uterine Cancer Treatment
Medical advancements are continuously improving the diagnosis and treatment of uterine cancer. Here are some promising areas:
Immunotherapy
Checkpoint Inhibitors: These drugs help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. They have shown promise in treating various types of cancer, including uterine cancer.
Vaccine Therapy: Researchers are developing vaccines that stimulate the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
Genetic Testing and Personalized Medicine
BRCA and Lynch Syndrome Testing: Identifying genetic mutations can help tailor treatment plans and preventive measures for patients and their families.
Molecular Profiling: Analyzing the molecular characteristics of a tumor can guide the selection of targeted therapies.
Advocacy and Awareness
Advocacy and raising awareness about uterine cancer are crucial for improving early detection, treatment, and patient support.
Raising Awareness
Educational Campaigns: Public awareness campaigns educate women about the symptoms of uterine cancer and the importance of regular screenings.
Community Events: Events such as health fairs, walks, and seminars can spread awareness and raise funds for research.
Legislative Advocacy
Policy Changes: Advocates work to influence healthcare policies to improve access to care, funding for research, and support services for cancer patients.
Patient Rights: Ensuring that patients have access to the necessary treatments and support, regardless of their financial situation.
The journey through uterine cancer involves many facets, including medical treatment, emotional support, and practical assistance. Advances in research and personalized medicine continue to improve outcomes and offer hope to those affected by this disease.
Caregivers, healthcare providers, and support networks play essential roles in supporting patients throughout their journey. By staying informed, seeking support, and maintaining a proactive approach to health, patients and their loved ones can navigate the challenges of uterine cancer with resilience and strength.
Remember, you are not alone. There are many resources and communities ready to support you every step of the way. Whether you are a patient, a survivor, or a caregiver, your well-being matters, and there is help available to guide you through this journey. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against uterine cancer.
Survivorship and Long-Term Care
Living beyond a uterine cancer diagnosis brings a new set of challenges and opportunities for long-term health and well-being. Here are some important aspects to consider:
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular Check-Ups: Routine follow-up appointments with your oncologist and healthcare team are essential for monitoring your health and catching any signs of recurrence early.
Surveillance Plans: Your healthcare provider will develop a surveillance plan tailored to your specific situation, which may include periodic imaging tests, physical exams, and lab tests.
Managing Late Effects: Some treatments may cause long-term side effects, such as hormonal changes or cardiovascular issues. Regular monitoring and early intervention can help manage these effects.
Health Maintenance
Healthy Diet: Continue to eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This supports overall health and recovery.
Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity to maintain strength, improve mood, and reduce the risk of recurrence. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program.
Mental Health: Prioritize your mental health by seeking counseling or support groups if needed. Managing stress, anxiety, and depression is crucial for long-term well-being.
Reproductive Health and Family Planning
For women of childbearing age, uterine cancer treatment can impact fertility. Here are some considerations:
Fertility Preservation
Pre-Treatment Counseling: Discuss fertility preservation options with your healthcare provider before starting treatment. Options may include egg or embryo freezing.
Specialist Consultation: Consult with a fertility specialist to explore available options and develop a personalized plan.
Post-Treatment Family Planning
Alternative Methods: If treatment affects fertility, consider alternative family-building options such as adoption, surrogacy, or donor eggs.
Hormonal Therapies: If you experience early menopause due to treatment, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be an option to manage symptoms. Discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
Advocacy and Research Participation
Engaging in advocacy and research can be empowering and help improve outcomes for others facing uterine cancer.
Advocacy Involvement
Join Organizations: Become involved with cancer advocacy organizations to raise awareness and support policy changes.
Share Your Story: Sharing your experience through blogs, social media, or public speaking can provide support to others and highlight the importance of early detection and treatment.
Fundraising and Events: Participate in fundraising events and campaigns to support cancer research and patient services.
Research Participation
Clinical Trials: Consider participating in clinical trials to contribute to the advancement of uterine cancer treatment and care.
Research Studies: Get involved in research studies that aim to understand the long-term effects of cancer treatment and improve survivorship care.
Building a Support Network
A strong support network is invaluable for navigating life after uterine cancer.
Family and Friends
Open Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with your loved ones. Sharing your feelings and experiences can strengthen your support system.
Ask for Help: Don’t hesitate to ask for help with daily tasks, transportation to appointments, or emotional support.
Support Groups and Counseling
Join Groups: Look for local or online support groups where you can connect with others who have had similar experiences.
Professional Counseling: Seek professional counseling if you need help managing the emotional and psychological impacts of your diagnosis and treatment.
Embracing a New Normal
Adapting to life after uterine cancer involves finding a new normal and focusing on personal growth and well-being.
Setting Goals
Personal Goals: Set achievable personal goals that focus on your interests, hobbies, and passions. This can provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
Health Goals: Establish health-related goals, such as maintaining a healthy weight, improving fitness, or quitting smoking.
Celebrating Milestones
Acknowledge Achievements: Celebrate milestones in your recovery and survivorship journey. Recognize your strength and resilience.
Stay Positive: Maintain a positive outlook and focus on the progress you’ve made. Surround yourself with supportive and uplifting influences.
Living with and beyond uterine cancer involves a comprehensive approach that addresses medical, emotional, and practical aspects of life. With ongoing medical advancements, personalized care, and strong support networks, individuals affected by uterine cancer can achieve better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. There are numerous resources and support systems available to help you navigate each step. By staying informed, seeking support, and focusing on your well-being, you can face the challenges of uterine cancer with strength and resilience.
Together, we can continue to make strides in the fight against uterine cancer, bringing hope and better futures to those affected by this disease.
FAQs on Tests to Diagnose Uterine Cancer
1. What are the common tests used to diagnose uterine cancer?
Answer: The common tests used to diagnose uterine cancer include:
- Pelvic Exam: A physical examination of the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic organs.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: An imaging test where an ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina to create images of the uterus and ovaries.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A procedure where a small sample of the uterine lining is removed and examined for cancer cells.
- Hysteroscopy: A procedure where a thin, lighted tube is inserted into the uterus through the vagina to inspect the inside of the uterus and take tissue samples.
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): A surgical procedure to remove tissue from the inside of the uterus for examination.
2. What is a transvaginal ultrasound, and why is it used?
Answer: A transvaginal ultrasound is an imaging test where an ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina to obtain detailed images of the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic organs. It is used to detect abnormalities in the uterine lining, such as thickening or masses, which may indicate the presence of cancer or other conditions.
3. How is an endometrial biopsy performed?
Answer: During an endometrial biopsy, a thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. A small sample of the endometrial tissue is then suctioned out and sent to a lab for analysis. This procedure is usually performed in a doctor’s office and may cause some discomfort or cramping.
4. What is hysteroscopy, and how does it help in diagnosing uterine cancer?
Answer: Hysteroscopy is a procedure that involves inserting a thin, lighted tube (hysteroscope) through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. This allows the doctor to directly view the inside of the uterus and take tissue samples if necessary. Hysteroscopy helps identify abnormal growths or areas that may require further testing.
5. When is dilation and curettage (D&C) necessary?
Answer: Dilation and curettage (D&C) is performed when a more comprehensive sample of the uterine lining is needed, or when an endometrial biopsy results are inconclusive. It involves dilating the cervix and scraping the uterine lining with a curette to remove tissue for examination. D&C is typically done in a hospital or surgical center.
6. Are these diagnostic tests painful?
Answer: Some discomfort or cramping is common during procedures like endometrial biopsy, hysteroscopy, and D&C. Pain levels vary among individuals. Doctors often recommend taking over-the-counter pain relievers before and after the procedures to help manage discomfort.
7. How should I prepare for these diagnostic tests?
Answer: Preparation for these tests may vary. For a transvaginal ultrasound, you may be asked to empty your bladder before the test. For procedures like hysteroscopy or D&C, you might need to follow specific instructions regarding eating, drinking, and medications. Your healthcare provider will give you detailed preparation guidelines.
8. What are the risks associated with these diagnostic tests?
Answer: While these tests are generally safe, there are some risks involved, such as infection, bleeding, or injury to the uterus. These complications are rare. Your healthcare provider will discuss the risks and benefits with you before the procedure.
9. How long does it take to get the results from these tests?
Answer: The time to receive results can vary. For biopsies, it may take a few days to a week for the lab to analyze the tissue samples. Your healthcare provider will inform you when to expect the results and will discuss them with you during a follow-up appointment.
10. What happens if the test results indicate uterine cancer?
Answer: If the test results indicate uterine cancer, your healthcare provider will discuss the diagnosis with you and outline the next steps. This typically involves further imaging tests to determine the stage of the cancer, followed by developing a treatment plan that may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other treatments.
11
. How accurate are these diagnostic tests for uterine cancer?
Answer: Diagnostic tests for uterine cancer are generally accurate, but no test is 100% reliable. Transvaginal ultrasounds and endometrial biopsies are effective in detecting abnormalities, but sometimes additional tests like hysteroscopy or D&C are necessary to confirm the diagnosis. If results are inconclusive, your healthcare provider may recommend further testing or repeat procedures.
12. Can these tests detect other conditions besides uterine cancer?
Answer: Yes, these tests can detect other conditions affecting the uterus and pelvic organs, such as endometrial hyperplasia, fibroids, polyps, and infections. An accurate diagnosis helps determine the appropriate treatment for any underlying conditions.
13. Are there any alternatives to these tests?
Answer: While the mentioned tests are standard for diagnosing uterine cancer, your healthcare provider might suggest alternatives or additional tests based on your specific situation. Alternatives can include MRI or CT scans for detailed imaging or blood tests to check for tumor markers.
14. What should I do if I experience symptoms after the tests?
Answer: It’s normal to experience mild cramping, spotting, or light bleeding after procedures like endometrial biopsy or D&C. However, if you experience severe pain, heavy bleeding, fever, or signs of infection, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
15. How often should these diagnostic tests be repeated?
Answer: The frequency of repeat testing depends on your individual risk factors and previous test results. If you have a history of abnormal results or are at high risk for uterine cancer, your healthcare provider may recommend more frequent monitoring.
16. Can lifestyle changes affect the results of these tests?
Answer: Lifestyle changes generally do not affect the immediate results of diagnostic tests for uterine cancer. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall reproductive health and may reduce your risk of developing cancer or other conditions.
17. What questions should I ask my healthcare provider about these tests?
Answer: Here are some important questions to ask:
- Why is this test necessary for my condition?
- How should I prepare for the test?
- What will happen during the test?
- What are the potential risks and side effects?
- How long will it take to get the results?
- What are the next steps if the results are abnormal?
- Are there any alternative tests available?
18. How can I support myself emotionally while awaiting test results?
Answer: Waiting for test results can be stressful. To support yourself emotionally, consider:
- Talking to friends or family members about your concerns.
- Joining a support group for individuals facing similar health issues.
- Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Keeping yourself busy with hobbies or activities you enjoy.
- Seeking professional counseling if you find it difficult to manage anxiety or stress.
By staying informed and proactive about your health, you can better navigate the diagnostic process and take steps toward effective treatment and management of uterine cancer.
Early Biomarkers for Detecting Uterine Malignancy
1. CA-125
Function: CA-125 is a protein that can be elevated in the blood of women with certain types of cancers, including endometrial cancer.
Usage: While CA-125 is not specific to uterine cancer and can be elevated in other conditions, monitoring CA-125 levels over time can be useful in detecting recurrence or progression of the disease.
2. HE4 (Human Epididymis Protein 4)
Function: HE4 is a protein that, when elevated, has been associated with certain types of cancers, including endometrial cancer.
Usage: HE4, when used in combination with other markers like CA-125, may improve the sensitivity and specificity of detecting uterine malignancies.
3. PAX-2 (Paired Box Gene 2)
Function: PAX-2 is a protein that plays a role in the development of the female reproductive system and is expressed in normal endometrial tissue.
Usage: Abnormal expression of PAX-2 has been linked to endometrial cancer and may serve as a potential biomarker for early detection.
4. PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog)
Function: PTEN is a tumor suppressor gene that is often mutated or inactivated in endometrial cancer.
Usage: Detection of PTEN mutations or inactivation may serve as an early biomarker for identifying individuals at risk of developing uterine malignancy.
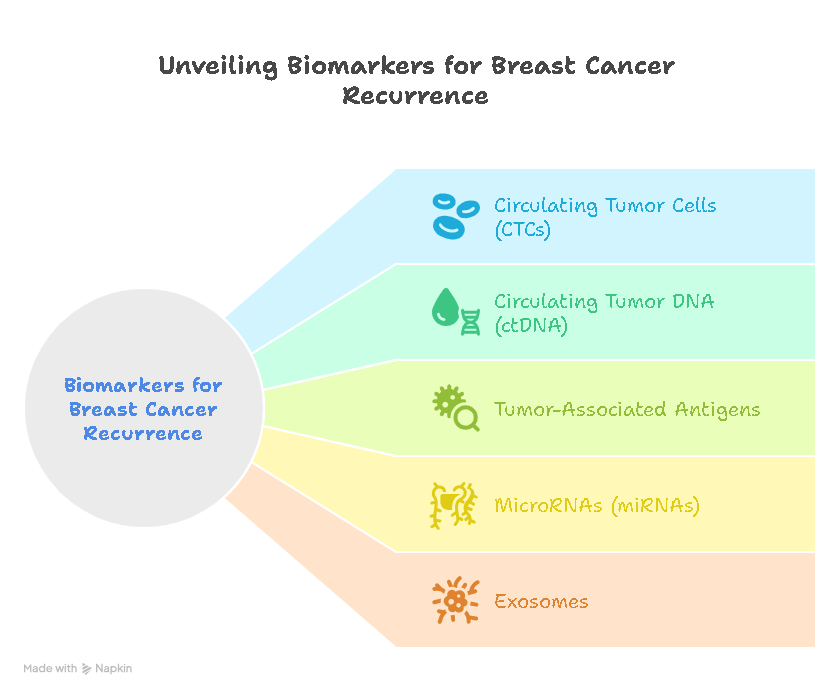
5. MicroRNAs
Function: MicroRNAs are small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression and have been found to be dysregulated in various cancers, including endometrial cancer.
Usage: Specific microRNA profiles may serve as biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of uterine malignancies.
6. DNA Methylation
Function: DNA methylation is a process that regulates gene expression and is often altered in cancer, including endometrial cancer.
Usage: Aberrant DNA methylation patterns in specific genes may serve as biomarkers for early detection and risk assessment of uterine malignancy.
7. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
Function: CTCs are cancer cells that have detached from the primary tumor and circulate in the bloodstream.
Usage: Detection and analysis of CTCs may provide valuable information about tumor characteristics and treatment response in uterine malignancies.
8. Imaging Biomarkers
Function: Imaging biomarkers, such as certain patterns seen on ultrasound, MRI, or PET scans, can indicate the presence of a tumor or changes in the uterus suggestive of malignancy.
Usage: These imaging biomarkers can aid in the early detection and diagnosis of uterine cancer, especially when used in combination with other biomarkers and clinical evaluation.
Early detection of uterine malignancies is crucial for improving patient outcomes. While further research is needed to validate these biomarkers for routine clinical use, they hold promise for enhancing early detection, risk assessment, and monitoring of uterine malignancies.
Can Tamoxifen Cause Uterine Cancer?
Tamoxifen is a medication commonly used to treat breast cancer, particularly hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. While tamoxifen is effective in reducing the risk of breast cancer recurrence, it has been associated with an increased risk of developing uterine cancer, specifically endometrial cancer.
Mechanism of Action
Tamoxifen works by blocking the effects of estrogen in breast tissue, which helps prevent the growth of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer cells. However, tamoxifen can have estrogen-like effects on the uterus, leading to changes in the endometrium (the lining of the uterus) that can increase the risk of developing endometrial cancer.
Risk Factors
The risk of developing uterine cancer with tamoxifen use is higher in postmenopausal women and those with certain risk factors, including:
- Long-term tamoxifen use (usually after 5 years)
- Age (risk increases with older age)
- Obesity
- Previous history of endometrial hyperplasia or cancer
- Use of estrogen replacement therapy
Monitoring and Prevention
To monitor for potential uterine changes, women taking tamoxifen should undergo regular gynecological exams and report any abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge to their healthcare provider promptly. Endometrial thickness may be monitored by ultrasound in some cases.
While tamoxifen is an important medication in breast cancer treatment and prevention, it is essential for women taking tamoxifen to be aware of the potential risks, including the increased risk of developing uterine cancer. Close monitoring and regular gynecological care can help detect any uterine changes early and manage them appropriately. Any concerns about the risks and benefits of tamoxifen should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Risk and Benefit Assessment
Before starting tamoxifen treatment, healthcare providers typically assess the individual’s risk factors for developing uterine cancer and weigh them against the potential benefits of the medication in treating breast cancer. Factors such as age, menopausal status, family history of uterine cancer, and overall health are considered.
Regular Monitoring
During tamoxifen treatment, regular gynecological exams and pelvic screenings are essential for monitoring any changes in the uterus. Women are advised to report any unusual symptoms such as vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, or discharge promptly to their healthcare provider.
Management of Uterine Changes
If uterine changes are detected, further evaluation may be necessary, including imaging tests such as ultrasound or biopsy to determine the nature of the changes. In some cases, discontinuing tamoxifen or switching to an alternative treatment may be considered.
Alternative Treatments
For women at high risk of uterine cancer or those who cannot tolerate the risks associated with tamoxifen, alternative treatments may be recommended. These may include other hormonal therapies or non-hormonal treatments for breast cancer.
Shared Decision-Making
The decision to use tamoxifen should be based on a thorough discussion between the woman and her healthcare provider, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment. It is essential for women to be well-informed about the risks of uterine cancer associated with tamoxifen and to actively participate in the decision-making process regarding their treatment.
Conclusion
While tamoxifen is an effective treatment for breast cancer, it is associated with an increased risk of developing uterine cancer, particularly endometrial cancer. Close monitoring and early detection of uterine changes are essential for women taking tamoxifen. By working closely with their healthcare providers and being vigilant about any symptoms, women can reduce the risks associated with tamoxifen use and receive appropriate care if uterine changes occur.







Leave a Reply