Introduction
Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent and deadly forms of cancer affecting women worldwide. Over the years, significant progress has been made in understanding the disease, leading to better diagnosis and treatment options. Among the groundbreaking advancements in breast cancer research are biomarkers, which play a crucial role in identifying and managing the disease effectively.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- 2.1 What are Biomarkers?
- 2.2 Types of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- The Importance of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- 3.1 Early Detection and Diagnosis
- 3.2 Personalized Treatment Plans
- 3.3 Monitoring Treatment Efficacy
- Common Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- 4.1 Hormone Receptor Status
- 4.2 HER2/neu Protein
- 4.3 Ki-67 Protein
- 4.4 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes
- 4.5 p53 Protein
- Testing and Interpretation of Biomarker Results
- 5.1 Biopsy and Tissue Testing
- 5.2 Genetic Testing
- 5.3 Interpreting Biomarker Results
- Advances in Breast Cancer Biomarker Research
- 6.1 Liquid Biopsies
- 6.2 Circulating Tumor Cells
- 6.3 Genomic Profiling
- Challenges and Limitations of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- 7.1 False Positives and False Negatives
- 7.2 Standardization of Testing
- 7.3 Ethical Considerations
- Promising Future of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- 8.1 Predicting Treatment Response
- 8.2 Identifying Recurrence Risk
- 8.3 Targeting Cancer Stem Cells
- Lifestyle Choices to Reduce Breast Cancer Risk
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- 11.1 What is the role of estrogen receptor status as a breast cancer biomarker?
- 11.2 Can biomarkers help in early breast cancer detection?
- 11.3 Are biomarker tests expensive?
- 11.4 How often should biomarker testing be done?
- 11.5 Can biomarkers predict breast cancer recurrence?

Understanding Breast Cancer Biomarkers
2.1 What are Biomarkers?
Biomarkers are measurable biological indicators that can be found in the blood, tissues, or other bodily fluids. They provide essential information about the presence and behavior of cancer cells. In the context of breast cancer, biomarkers offer valuable insights into the tumor’s characteristics and can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
2.2 Types of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
Several types of breast cancer biomarkers exist, each with unique functions. These include hormone receptors, proteins, and genes associated with breast cancer development and progression.
The Importance of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
3.1 Early Detection and Diagnosis
One of the most significant advantages of breast cancer biomarkers is their role in early detection. Biomarker tests can identify breast cancer even before physical symptoms manifest, allowing for timely intervention and improved treatment outcomes.
3.2 Personalized Treatment Plans
Every breast cancer patient is unique, and biomarkers enable oncologists to tailor treatment plans to each individual’s specific needs. Personalized therapies offer better chances of success and reduced side effects.
3.3 Monitoring Treatment Efficacy
Biomarkers also serve as essential tools in monitoring treatment effectiveness. By regularly testing biomarker levels during therapy, healthcare professionals can assess how well the treatment is working and make adjustments as needed.
Common Breast Cancer Biomarkers
4.1 Hormone Receptor Status
Hormone receptor status, including estrogen and progesterone receptors, is a vital breast cancer biomarker. These receptors influence the tumor’s growth and help determine whether hormone therapy will be effective.
4.2 HER2/neu Protein
The HER2/neu protein plays a critical role in cell growth and division. Its overexpression is associated with aggressive breast cancer, but targeted therapies like Herceptin have proven effective in HER2-positive cases.
4.3 Ki-67 Protein
Ki-67 is a protein associated with cell proliferation. High Ki-67 levels may indicate a faster-growing tumor, affecting treatment decisions.
4.4 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes
Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are strongly linked to hereditary breast cancer. Identifying these mutations helps assess the risk of developing breast cancer.
4.5 p53 Protein
The p53 protein is a tumor suppressor, and its inactivation is linked to cancer development. Understanding p53 status can aid in treatment selection.
Testing and Interpretation of Biomarker Results
5.1 Biopsy and Tissue Testing
Biopsies remain a cornerstone in determining breast cancer biomarkers. Tissue samples are examined to identify specific biomarker expression.
5.2 Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can identify inherited mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, providing critical information for patients and their families.
5.3 Interpreting Biomarker Results
Interpreting biomarker test results requires expertise. Oncologists analyze the data to create individualized treatment plans.
Advances in Breast Cancer Biomarker Research
6.1 Liquid Biopsies
Liquid biopsies are a non-invasive method of detecting biomarkers using blood samples. This approach offers a promising avenue for early detection and monitoring.
6.2 Circulating Tumor Cells
Circulating tumor cells in the bloodstream may hold valuable information about the tumor’s behavior and response to treatment.
6.3 Genomic Profiling
Genomic profiling allows for a comprehensive analysis of a tumor’s genetic makeup, aiding in treatment selection.
Challenges and Limitations of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
7.1 False Positives and False Negatives
Biomarker tests are not infallible, and false positives or false negatives may occur, leading to potential misdiagnoses or incorrect treatment choices.
7.2 Standardization of Testing
Standardizing biomarker testing protocols is essential to ensure consistency and accuracy across different healthcare facilities.
7.3 Ethical Considerations
As biomarker research progresses, ethical issues surrounding patient privacy and data usage must be addressed.
Promising Future of Breast Cancer Biomarkers
8.1 Predicting Treatment Response
Advancements in biomarker research aim to predict how patients will respond to specific treatments, improving treatment success rates.
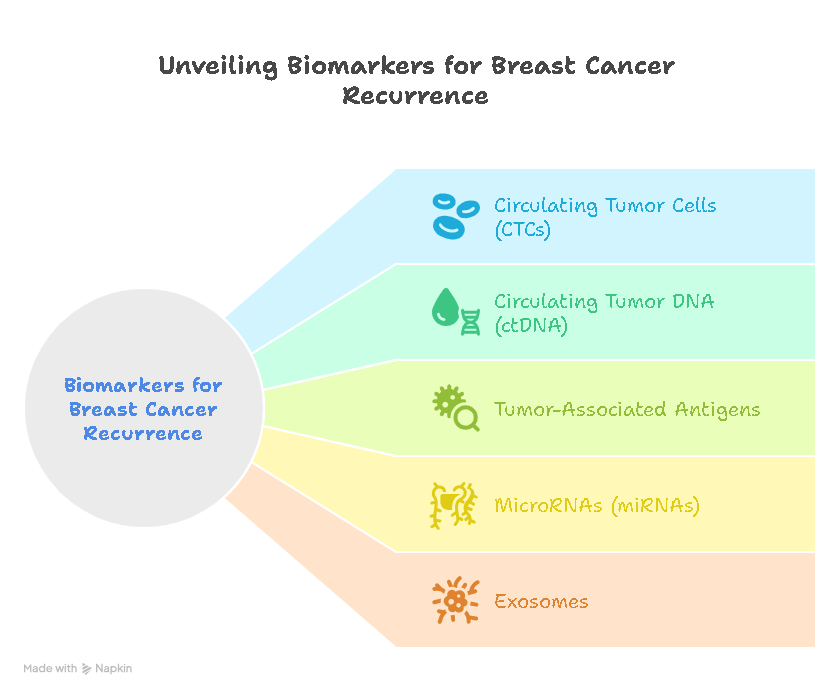
8.2 Identifying Recurrence Risk
Biomarkers are being studied to identify patients at a higher risk of cancer recurrence, enabling proactive management.
8.3 Targeting Cancer Stem Cells
Research is ongoing to target cancer stem cells, a small subset of cells with self-renewal capabilities, to prevent relapse.
Lifestyle Choices to Reduce Breast Cancer Risk
In addition to medical advancements, adopting a healthy lifestyle can also reduce breast cancer risk. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to overall well-being.
Conclusion
Breast cancer biomarkers have revolutionized how we approach the detection, diagnosis, and treatment of breast cancer. By providing essential insights into the disease’s behavior, biomarkers empower healthcare professionals to deliver personalized and effective treatment plans. Ongoing research in this field holds great promise for further improving breast cancer outcomes and ultimately defeating this formidable disease.
FAQs
11.1 What is the role of estrogen receptor status as a breast cancer biomarker?
Estrogen receptor status is crucial as it helps determine whether the tumor responds to hormone therapy. Positive estrogen receptor status indicates that hormones fuel the tumor’s growth, making hormone therapy an effective treatment option.
11.2 Can biomarkers help in early breast cancer detection?
Yes, biomarkers play a significant role in early breast cancer detection. Biomarker tests can identify cancer even before physical symptoms manifest, enabling timely intervention and improved outcomes.
11.3 Are biomarker tests expensive?
The cost of biomarker tests varies depending on the type of test and the healthcare provider. However, advances in technology may lead to increased accessibility and reduced costs in the future.
11.4 How often should biomarker testing be done?
The frequency of biomarker testing depends on individual circumstances and treatment plans. Oncologists may conduct tests at specific intervals to monitor treatment efficacy and assess any changes in the tumor’s behavior.
11.5 Can biomarkers predict breast cancer recurrence?
Researchers are actively exploring biomarkers’ potential to predict breast cancer recurrence. Identifying patients at a higher risk of recurrence would enable proactive measures to prevent or manage relapse more effectively.







Leave a Reply